Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Nakai, Kei*; Endo, Kiyoshi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*
Proceedings of 11th World Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ISNCT-11) (CD-ROM), 14 Pages, 2004/10
A dose distribution considered the tumor cell density distribution is required on the radiation therapy. We propose a novel method of determining target region considering the tumor cell concentration as a new function for the next generation Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) dosimetry system. It has not been able to sufficiently define the degree of microscopic diffuse invasion of the tumor cells peripheral to a tumor bulk in malignant glioma using current medical imaging. Referring to treatment protocol of BNCT, the target region surrounding the tumor bulk has been set as the region which expands at the optional distance with usual 2cm margin from the region enhanced on T1 weighted gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In this research, the cell concentration of the region boundary of the target was discussed by using tumor cell diffusion model in the sphere spatio-temporal system. The survival tumor cell density distribution after the BNCT irradiation was predicted by the two regions diffusion model for a virtual brain phantom.
Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(2), p.193 - 199, 2004/06
To investigate the possibility of experimental approach for dose evaluation using a realistic phantom that faithfully reproduced the shape of a head, this research considered the manufacture of a patient's realistic phantom and the reappearance of actual medical irradiation conditions. We selected the rapid prototyping technology to produce the realistic phantom from the Computed Tomography (CT) imaging. This phantom was irradiated under the same clinical irradiation condition of this patient, and the thermal neutron distribution on the brain surface was measured in detail. Several subjects on material and data conversion in the production of realistic phantom were mentioned. As a result of reproducing medical irradiation using the realistic phantom, the maximum thermal neutron flux became a value about 22% lower than the surface of the actual brain. If the problems pointed out in this paper are solved, it may also be expected that it would become possible to check computational dosimetry system.
Nakagawa, Yoshinobu*; Pooh, K. H.*; Kobayashi, Toru*; Kageji, Teruyoshi*; Uyama, Shinichi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Kumada, Hiroaki
Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 62(1), p.87 - 99, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:126 Percentile:83.31(Oncology)Our concept of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is selective destruction of tumor cells using the heavy-charged particles Yielded through 10B(n, alpha)7 Li reactions. In the analysis of side effects due to radiation, we included all the 159 patients treated between 1977 and 2001. With respect to the radiation dose (i.e. physical dose of boron n-alpha reaction), the new protocol prescribes a minimum tumor volume dose of 15Gy or, alternatively, a minimum target volume dose of 18Gy. The maximum vascular dose should not exceed 15Gy (physical dose of boron n-alpha reaction) and the total amount of gamma rays should remain below 10Gy, including core gamma rays from the reactor and capture gamma in brain tissue. The outcomes for 10 patients who were treated by the new protocol using a new mode composed of thermal and epithermal neutrons are reported.
Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Nakai, Kei*; Zhang, T.*; Matsushita, Akira*; Takano, Shingo*; Endo, Kiyoshi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.1073 - 1078, 2002/09
Since 1998 to 2002, a new clinical trial of an intraoperative boron neutron capture therapy (IOBNCT) at JRR-4 of Japan Atomic Energy Institute (JAERI) using BSH with mixed thermal/epithermal neutron beam has been accomplished. There have been 9 patients included in this study. The median survival time (MST) in GBM was 19.8 months and 16.8 months in AA. IOBNCT with mixed thermal/epithermal neutron beam provide better primary radiation effect than conventional therapy in selected cases. Our phase I/II clinical trial was effective in local tumor control. Further clinical trial with new design should be performed to prove the efficacy of IOBNCT.
Endo, Kiyoshi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kishi, Toshiaki; Torii, Yoshiya; Kashimura, Takanori*; Otake, Shinichi*
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.425 - 430, 2002/09
Using the Rapid Prototyping Technique, we produced a realistic phantom as a formative model of a patient head. This realistic phantom will contribute to verification of our planning system. However, cross-correlation among the calculations using the JAERI Computational Dosimetry System (JCDS), the realistic phantom, and the in vivo measurements were not fully completed because of the difficulty involved in modeling a post-surgical brain and a thermal neutron shield. The experimental simulation technique using the realistic phantom is a useful tool for more reliable dose planning for the intraoperative BNCT.
Matsushita, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Torii, Yoshiya; Kashimura, Takanori*; Otake, Shinichi*
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.141 - 143, 2002/09
A thermal-epithermal mixed beam "Thermal Neutron Beam Mode I" was used in the eleven sessions of boron neutron capture therapy which have been performed at JRR-4 from 1998. We are planning to use an epithermal beam for the treatment of deeper tumors in the next trial of the intraoperative BNCT. In this study, "Epi-12" which was made by putting up a cadmium shutter of "Thermal Neutron Beam Mode I" was investigated for the clinical benefits and safety by epithermal beams. Decrease of fast neutron contamination ratio in Epi-12 mode is the advantage for BNCT, particular in the intraoperative BNCT. Because fast neutron on the brain surface is one of the critical factors in the intraoperative BNCT in which the plain beam directly interacts the normal structures. Furthermore a mixture of mode Epi-12 and Th-12 will provide various dose distribution designs. It may be used as a new method to control the best distribution for individual tumors.
Sekine, Toshiaki
Radioisotopes, 46(9), p.670 - 674, 1997/09
no abstracts in English
*; ; Tone, Tatsuzo; Mizumoto, Motoharu
10th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conf. (10-PBNC), 2, p.1425 - 1431, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
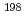 Au and
Au and 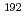 Ir sources for cancer therapy
Ir sources for cancer therapySato, Akira; Kogure, Hiroto;
JAERI-M 91-020, 83 Pages, 1991/02
no abstracts in English